In the fiercely competitive landscape of modern retail, delivering on consumer expectations with a seamless shopping experience across multiple channels has become imperative. The importance of real-time inventory visibility, offering alternative fulfillment options, and minimizing stockouts cannot be overstated, as they collectively contribute to creating truly seamless and satisfying customer experiences.
What are the different types of retail omnichannel?
Retailers can employ a variety of strategies to effectively engage with customers through different types of retail omnichannel approaches:
- Buy Online and Pickup In-Store (BOPIS): This strategy allows customers to place orders online and then pick up their purchases at a physical store.
- Online to In-Store (Reserve and Try): In this approach, customers can browse products and make a reservation online, ensuring that the items are available for them to try on or purchase in-store.
- Ship from Store: This strategy involves using physical stores as distribution centers. When an online order is placed, the retailer can fulfill it by shipping products directly from a local store, reducing shipping times and costs. It maximizes inventory utilization and provides quicker delivery options.
- Endless Aisle: Retailers implement endless aisle strategies to offer a wider range of products in-store, even if they’re not physically present. Through digital kiosks, tablets, or mobile apps, customers can browse and order products that are available online but not in-store.
- Unified Customer Profiles: Creating a single, unified customer profile that spans all channels allows retailers to provide personalized experiences. Whether a customer interacts through social media, a mobile app, or in-store, their preferences, purchase history, and other relevant data can be used to tailor their experience.
- Mobile Commerce: As mobile usage continues to grow, providing a seamless shopping experience across mobile devices is crucial. Retailers can develop mobile apps or optimize their websites for mobile shopping, ensuring a consistent and user-friendly experience.
- Social Commerce: Leveraging social media platforms for shopping is another way to integrate channels. Retailers can showcase products on platforms like Instagram or Facebook and enable customers to purchase directly through those channels.
- Voice Commerce: With the rise of voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant, retailers can create voice-commerce experiences that allow customers to shop using voice commands, making the shopping journey more convenient.
- IoT-Enabled Shopping: The Internet of Things (IoT) can enhance the omnichannel experience by enabling devices to communicate with each other. For instance, customers can receive personalized offers on their smartphones while in-store based on their location and purchase history.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): Integrating VR or AR technology can allow customers to virtually try products before purchasing, creating an interactive and engaging shopping experience.
Leveraging these strategies, retailers can offer a consistent, convenient, and personalized experience that enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What are Omnichannel Retail Capabilities?
omnicanal capabilities refer to the integration and coordination of various sales channels, such as physical stores, eCommerce websites, mobile apps, kiosks, call centers, and catalogs.
This can be achieved with Oracle Retail suit of Omnichannel components such as Oracle Retail Xstore, Oracle Retail Order Broker Cloud Service, Oracle Retail Order Management Cloud Service, Oracle Retail Merchandizing Cloud Service, Oracle Retail Store Inventory Operations Cloud Service and interfaces with Omnichannel Cloud Data Service and Oracle Cloud SOA.
The Oracle Retail Xstore Point of Service is an industry-leading point-of-sale application that is designed to enable retailers to manage omnichannel orders efficiently, optimize inventory usage, reduce inventory shortages, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
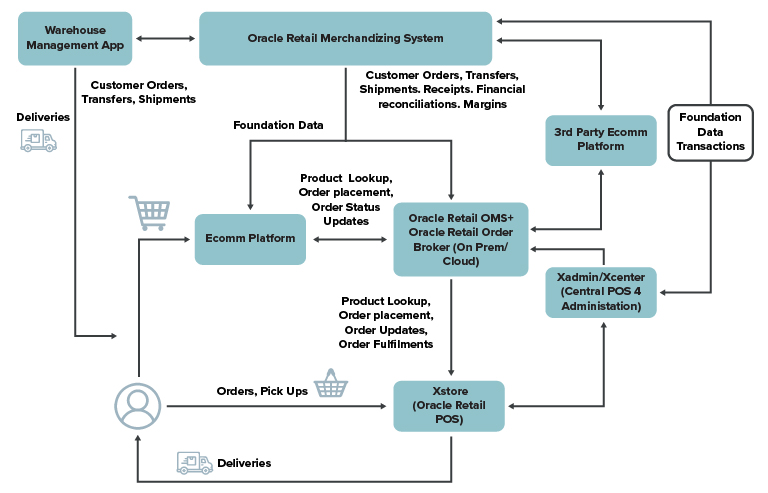
Oracle Retail Xstore Point of Service (POS) for seamless omnichannel experiences:
Oracle Xstore and Order Broker applications are part of Oracle’s omnichannel solution components. They empower retailers to initiate, process, and complete omnichannel order journeys from their physical stores. Oracle Xstore is seamlessly integrated with Oracle Retail Order Broker (OROB), to enable intelligent order routing and reduced stockouts, to ensure quick turnaround for orders, optimal inventory usage, and reduced operational overheads. It also empowers sales associates to quickly and easily view inventory location and offer alternative fulfillment methods, such as direct shipment from another location, or to schedule a store pick-up.
Connect with us for free POS Assessment.
Key Features of Oracle Xstore POS for Omnichannel Retail
Real-time Inventory Knowledge: Oracle Xstore, integrated with Oracle Retail Order Broker, provides real-time inventory updates, allowing sales associates to offer alternative fulfillment options to customers even if the merchandise is out of stock at the current location.
Omnichannel Order Routing: Through the integration of Oracle Retail Xstore and Oracle Retail Order Broker (OROB), orders are intelligently routed based on factors such as inventory availability, distance, and predefined routing configurations. Retailers across various platforms can use Order Broker APIs to check inventory and place different types of orders. There is an overnight feed configured from Xcenter to OROB through which product and product location mapping data can be interfaced to OROB either in a flat file or through an API call.
The Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) serves as a central storage for merchandising and pricing data essential to Oracle Retail Omnichannel Applications like Order Broker and Customer Engagement. OCDS is part of the Oracle Retail Integration Cloud Service, along with other technologies like Oracle Retail Bulk Data Integration (BDI) and Oracle Retail Integration Bus (RIB). OCDS gets its core merchandising data from Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS). Initial data loading is done through BDI, and subsequent updates are communicated through RIB messages. This data encompasses elements such as merchandise and organizational hierarchies, store and warehouse locations, items, tax rules, dimensions, and initial prices.
Order Orchestration: Typically, Order once placed through any platform – Ecomm Platform – web or mobile app, POS application – desktop or Mobile, 3rd party website, goes through a routing check and sourcing location selection basis, delivery address/pick up address proximity from sourcing location, Sourcing location inventory levels, Zone Routing, back order availability and order processing loads and other routing configurations in Order Broker. The Order Line information is interfaced to Sourcing and Fulfillment location that includes, Customer information, Pick Up and Delivery Address Details, Order Line, and Payment information. In a standard order life cycle, Order Line status moves from Open to New, Accepted, Picked, In Transit, and Ready for Pick Up or Fulfilled or Cancelled Statuses.
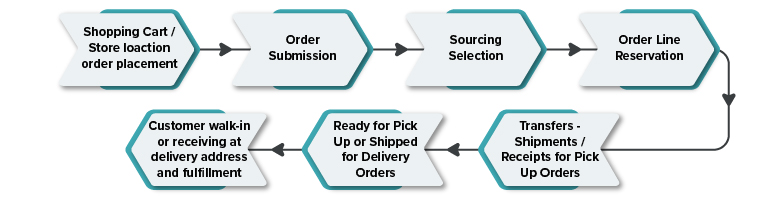
Inventory Movement Visibility: Xstore allows seamless visibility into inventory movements and transfers between locations, ensuring efficient order fulfillment and minimizing the risk of lost sales.
When Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management (ORSIM) application is integrated with OROB to enable seamless omnichannel experiences, inventory updates can be triggered to be interfaced with ORSIM (Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management).
Order Status Management: Retailers can easily manage order statuses for various types of orders, including delivery orders, and same or other store pickup orders, ensuring smooth order processing and customer communication.
Within the Xstore architecture, there’s a provision for rejecting and reassigning orders in cases where fulfillment isn’t feasible. In instances where pickup orders cannot be fulfilled, the order is refunded.
To facilitate the shipping of orders from the store for delivery, a connection between Xstore and local courier services is necessary. This integration ensures the generation of shipment IDs and tracking alerts.
Warehouse deliveries involve aspects such as managing inventory, generating invoices, and recording sales. APIs are utilized to manage updates related to the warehouse, handle transfers, and process cancellations independently of Xstore. For the transfer of product lines, a comprehensive process involving transfer orders, shipments, and the creation of receiving documents is employed.
Order Cancellations and Refunds: The Oracle Xstore architecture provides configurable options for order cancellations and refunds, thus preventing challenges associated with canceling orders after reservation and picking. Order Broker provides the feature of automatically canceling unclaimed orders, and it communicates the cancellation status to Xstore to initiate the necessary processes for cancellations and refunds. In the case of eCommerce orders, retailers need to make determinations regarding the reversal of online payments when handling order cancellations.
Notifications: Email notifications and order alerts play a crucial role in omnichannel retail, ensuring that customers are well-informed about their order details and the current status for all order line items.
At the same time, operational alerts help in quick turn-around for the orders and faster resolution of any issues at any stage in order life cycle. Xstore sends email alerts to customers for order receipts, order shipments, deliveries, order pick-ups, etc.
Order Broker also generates internal email alerts to the application administrator basis the event logging configured for probability rules, location product import, trace shopping logging, various API request responses for Order Broker, Vendor Portal, Drop Ship, and Inventory
Other Key configurations: Geographical zones can be set up to strategically limit order assignment and routing, optimizing logistics for cost-effective operations. To prevent a single location or few locations from being overburdened with heavy order processing, Order Broker has Maximum Daily Order assignment configuration. Here business can specify the maximum number of delivery or ship-for-pickup orders to be assigned to a location on a daily basis. If a location has met or exceeded the maximum number of orders for the day, the routing engine does not include the location in the product lookup search results for a delivery or ship-for-pickup order or does not assign the location during the original shopping or re-shopping for delivery or ship-for-pickup order. This helps in optimal order distribution across multiple locations. These restrictions apply irrespective of whether the location has inventory, or is flagged as Backorder Available.
The functionality of Order Broker encompasses order splitting, a measure that safeguards against revenue loss stemming from cancellations and refunds. To facilitate effective source selection, retailers can establish distinct location types and implement routing rules.
Marketplace and 3rd Party Platform Orders: Omnichannel orders encompass sale of merchandise through a retailer’s own channels and others, but also handlings orders and inventory movement. Retailers can even establish marketplaces, leveraging their inherent omnichannel capabilities to accept and seamlessly transfer orders.
When orders generated by third-party platforms are to be fulfilled from the retailer’s sourcing location, several considerations need to be addressed. These include invoicing for deliveries and pickups from fulfillment locations, managing order cancellations and refunds, interfacing discounts and payment information from original locations, creating transfers for warehouse locations, and factoring in margins for financial reconciliations.
Elevating Sales with Integrated Digital Microsites
Xstore’s impact on sales is amplified through the integration of a digital microsite via its Xcommerce feature. Store users gain access to an expansive product range by utilizing tablets or thin clients to explore items complete with images and alternative hierarchies. The flexibility to bundle products, source inventory, and convert to deliveries or pickups. All within the framework of existing payment and reporting processes further enhances sales potential.
With highly configurable Xstore and Order Broker applications, a retailer’s omnichannel journeys can be implemented with business-specific requirements. These journeys can be further enriched with the addition of Oracle Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) middleware. Business logic, routing, notifications can be implemented in Oracle SOA, along with setting requirements for creating transfers for warehouse-sourced orders.
Conclusion
Oracle Retail Xstore POS represents a game-changing solution for retailers aiming to thrive in today’s omnichannel retail landscape. Xstore’s powerful capabilities, when combined with Oracle Retail Order Broker, enable retailers to offer exceptional shopping experiences, enhance customer satisfaction, increase sales, and strengthen brand loyalty. By investing in Xstore’s seamless integrations and highly configurable functionalities, retailers can position themselves as leaders in the competitive retail industry, achieving retail excellence with every transaction.
SkillNet Oracle Retail Solutions
Since 2005, SkillNet SkillNet has been an Oracle Retail implementation partner and has achieved remarkable success by executing numerous retail transformation initiatives across NA, EMEA, LATAM, and APAC. Our expertise spans Oracle Omnichannel solutions – Stores, Merchandising, and Planning. We assist retailers at every stage of their digital evolution.
SkillNet has also created a suite of Oracle Retail Accelerators known as the Modern Commerce Engine. These accelerators are readily available for tasks ranging from implementation and upgrades to customized projects and continuous support for the Oracle Retail Suite. Tailoring our approach to each customer’s digital transformation journey, the SkillNet team harnesses these accelerators to enhance the quality of delivery, hasten time to market, and optimize costs.





 Engenharia
Engenharia